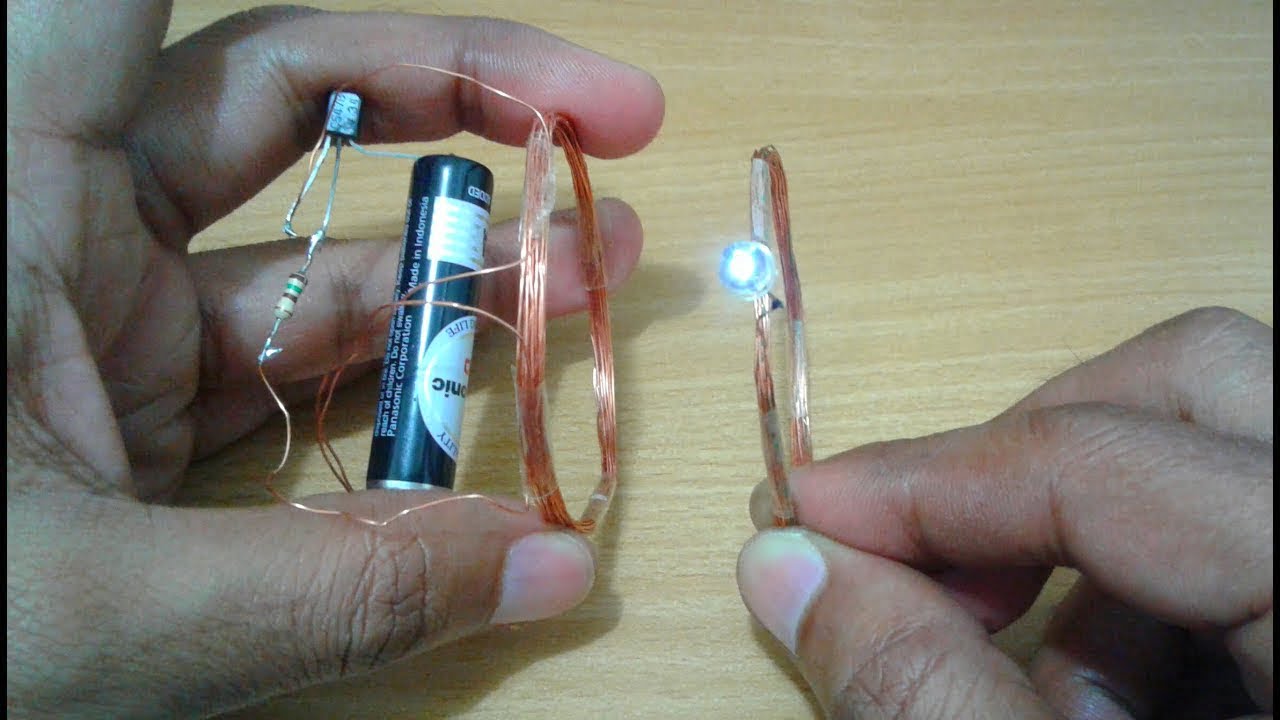
What Is Li-Fi Audio Transmission?
Hello Friends! Today we are going to perform an experiment on Li-Fi. First I’m going to tell you in brief about the Li-Fi project.
Li-Fi (short for light fidelity) is a wireless communication technology which utilizes light to transmit data and position between devices. The term was first introduced by Harald Haas during a 2011 TEDGlobal talk in Edinburgh.
In technical terms, the Li-Fi project is a light communication system that is capable of transmitting data at high speeds over visible light, ultraviolet, and infrared spectrums. In its present state, only LED lamps can be used for the transmission of visible light.
In terms of its end use, the technology is similar to Wi-Fi — the key technical difference being that Wi-Fi uses radio frequency to induce a voltage in an antenna to transmit data. Whereas Li-Fi uses the modulation of light intensity to transmit data. Li-Fi can theoretically transmit at speeds of up to 100 Gbit/s.
Li-Fi’s ability to safely function in areas otherwise susceptible to electromagnetic interference (e.g. aircraft cabins, hospitals, military) is an advantage. The technology is being developed by several organizations across the globe.
LiFi project is designed to use LED Light Bulbs similar to those present in our homes and offices. However, there is a slight difference between these LiFi LED Light Bulbs and Normal LED Light Bulbs. These LiFi LED Light Bulbs transmit Data through the Light given off by them and these Light Signals are received by Photoreceptors.
Now a question in your mind will arise what is a Photoreceptor? So in terms of Technology, a Photoreceptor is a Sensor that detects Light by capturing Photons (Photons are Light Particles)
Li-Fi Audio Transmission Circuit Diagram
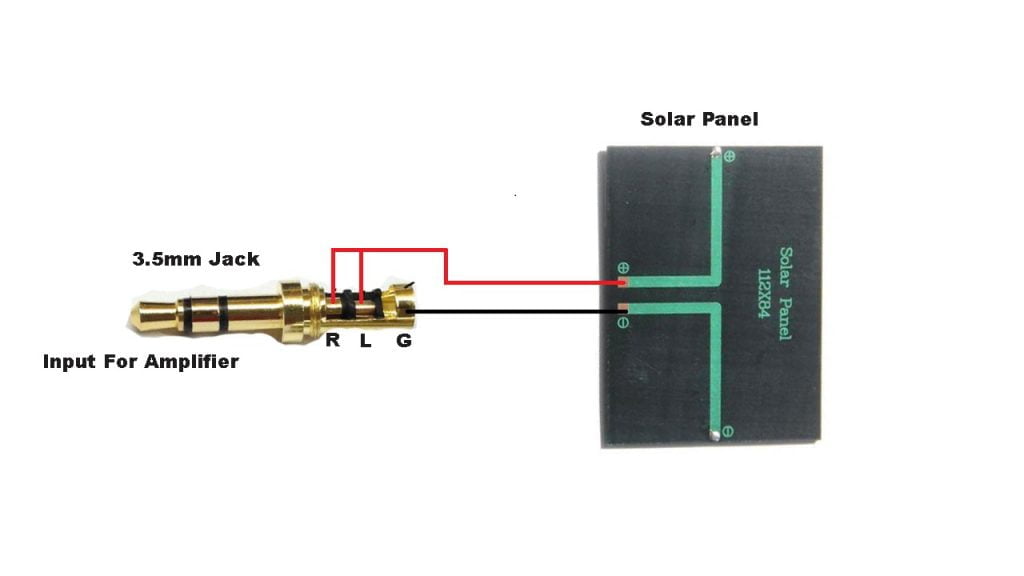
Wireless Power Transmission technology is old technology and it was demonstrated by “Nikola Telsa” ( Wireless electercity tesla ). Wireless power transmission mainly uses three main systems such as microwaves, solar cells Continue Reading…..
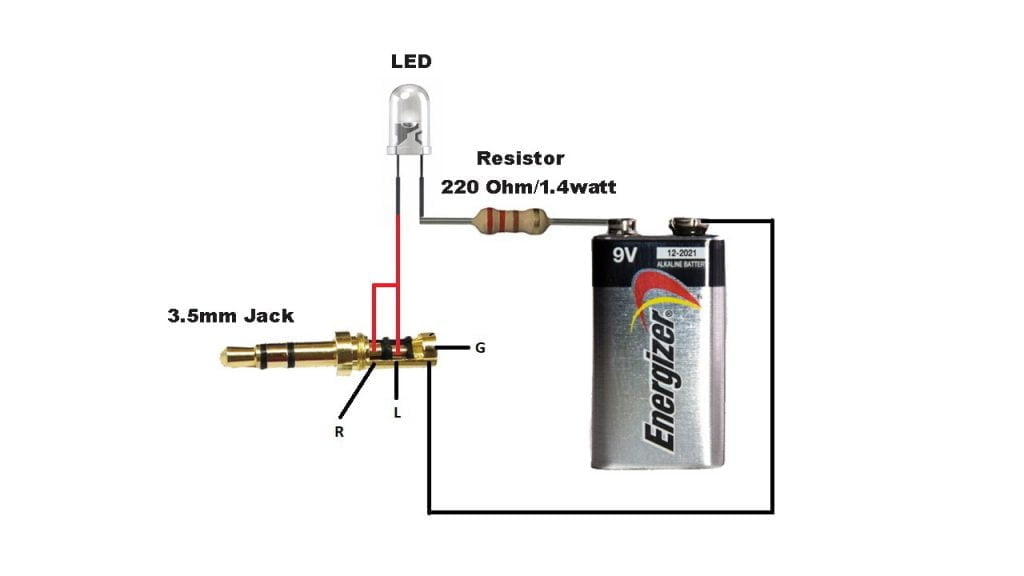

Parts list For Li-Fi Audio Transmission Project
- Resistor 220 Ohm/1.4 Watt – 1 Pc
- Audio Jack 3.5mm
- LED – 1Pc
- 9 Volt Battery


